The Gumball tool in Rhino is essential for speeding up your CAD modeling process. In this tutorial, we'll dive into how to use it effectively.
Tip: If you don't like reading, watch the video version of the tutorial here.
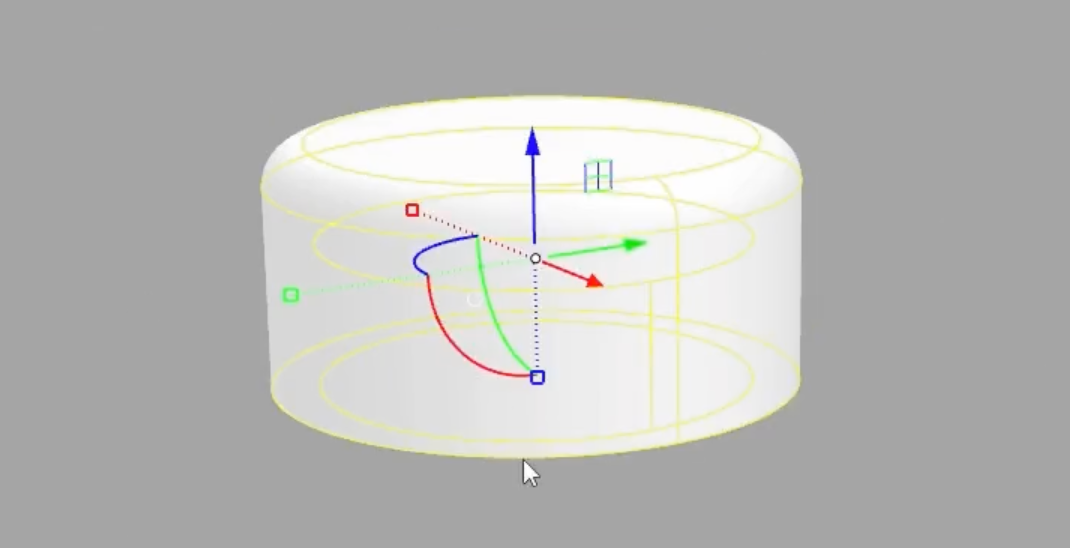
1. Identifying the Gumball Tool:
- The Gumball tool looks like a complex widget with multiple handles and arrows.
- It's commonly used for moving, translating, and rotating objects in Rhino.
- By default, the Gumball tool might be turned off. To activate it, look for the "Gumball" option in the lower section of the toolbar and toggle it on.
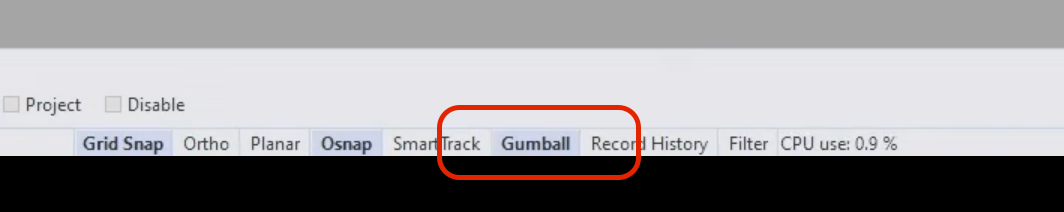
2. Traditional Movement Using the Move Tool:
- Navigate to the standard or transform toolbar.
- Select the "Move" tool.
- To move an object, click once for the origin and again for the final position.
- This is of course, the main way to move objects very precisely from one place to another.
- But this method has its drawbacks, especially when objects snap to unintended places in 3D space.
3. Where and when to use the Move tool:
- Ideal for moving objects to specific positions.
- To move an object to a new, precise location:
- Select the object.
- Activate the center point snap.
- Click on the center point of the object.
- Drag to the desired new position, ensuring it snaps correctly.
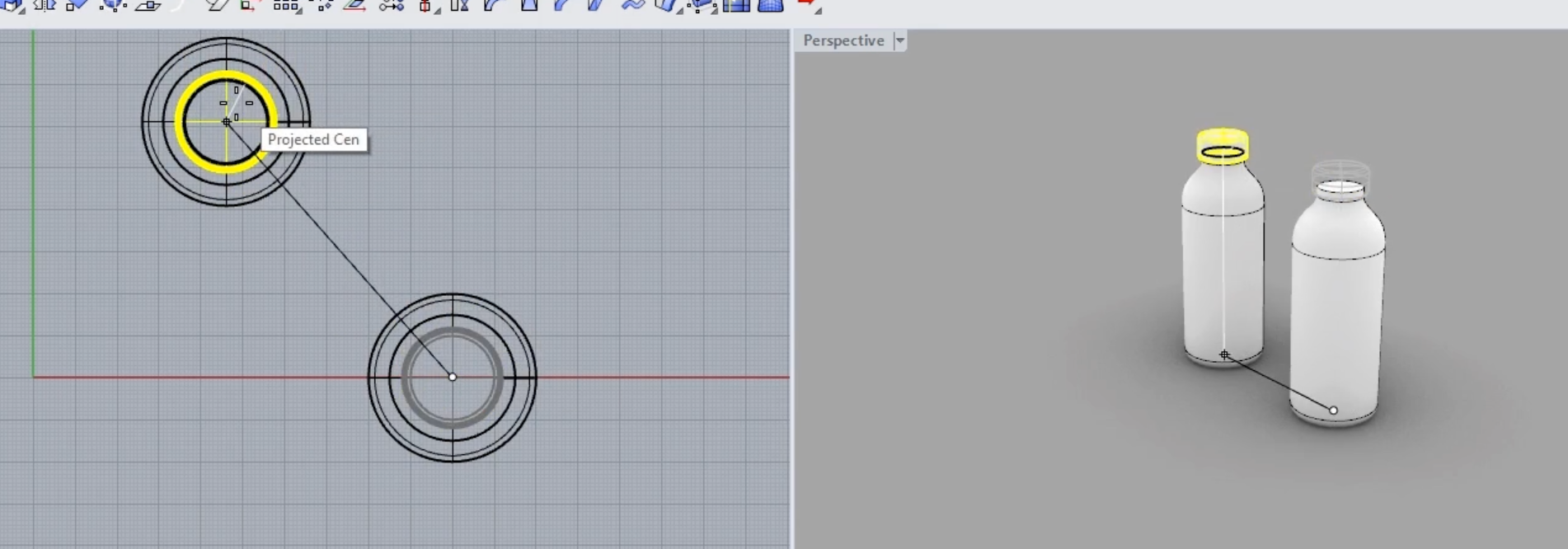
4. Introducing the Gumball for Efficient Iterations:
- The Gumball tool allows for rapid modifications and iterations of geometry.
- To create a new object using the Gumball:
- Create a cylinder (or any object).
- With the Gumball active, drag the cylinder while holding the Alt key to create a copy.
- Use the Gumball's scaling tool (holding Shift) to resize the object as needed.
- Monitor the dimensions in real-time with the measurements displayed during scaling.
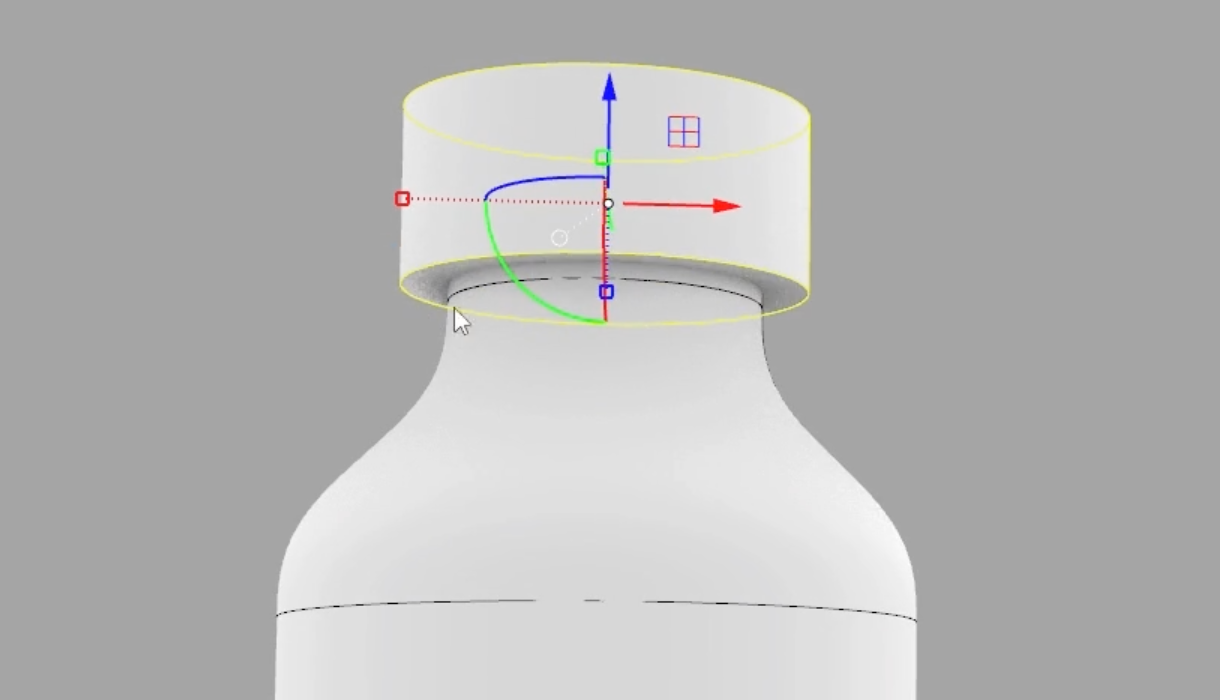
5. Advanced Gumball Operations:
- You can create completely new geometries just by utilizing the Gumball's features.
- Extract surfaces from an object.
- Delete unwanted parts.
- Use tools like "blend surface" to create new iterations of your design.
- Reuse parts of your design to create new components. For example:
- Copy and resize the top part of a cylinder using Alt + Shift.
- Adjust its height and position.
- Close any open parts using the "cap planar holes" option from the solid tools.
6. Using Grid Snap with the Gumball:
- By default, Gumball movements might be in one-millimeter increments due to the Grid Snap feature.
- If you need more gradual adjustments, deactivate the Grid Snap. This will allow for smoother and more precise changes.
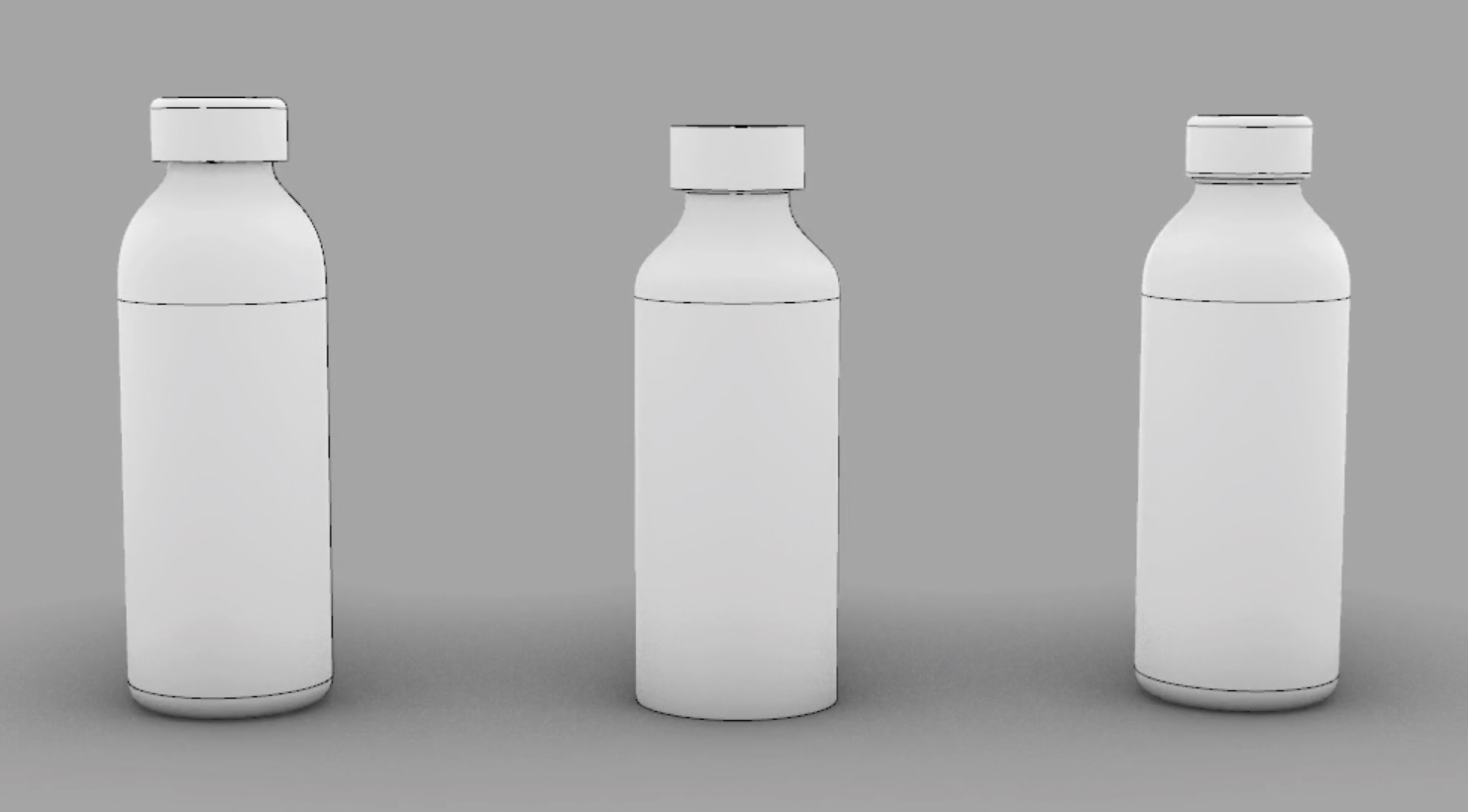
7. Practice:
Try creating various bottle designs using only the Gumball tool. With practice, your modeling speed and efficiency will greatly improve.

Conclusion:
The Gumball tool is a potent asset in Rhino, allowing for rapid design iterations and modifications. By mastering its features, you can enhance your CAD modeling process.
If you want to see any of the mentioned tips or tools in more detail, check out the video tutorial on YouTube.
Thanks for reading, and happy modeling!



Member discussion